Cognitive operate represents a key determinative issue for unbiased functioning among the many aged, particularly amongst these with age-related cognitive issues.
However; present pharmacotherapeutic ways for treating these issues present solely modest advantages on cognition.
The hypothalamic orexin (hypocretin) system is uniquely positioned, anatomically and functionally, to combine physiological features that assist correct cognition.
The ongoing paucity of orexin receptor agonists has mired the power to check their potential as cognitive enhancers. Fortunately, intranasal administration of native orexin peptides circumvents this challenge and others regarding peptide transport into the central nervous system (CNS).
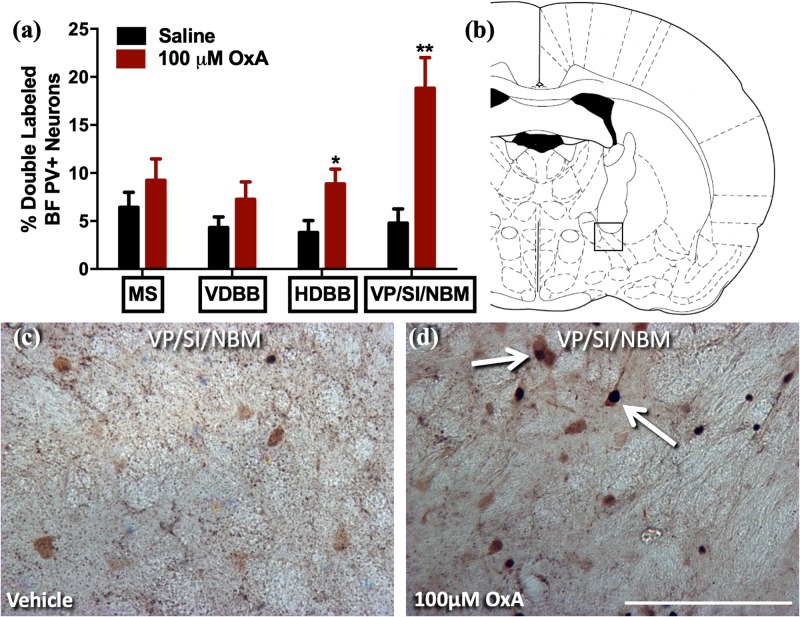
To examine the power of intranasal orexin-A (OxA) administration to enhance the anatomical, neurochemical, and behavioral substrates of age-related cognitive dysfunction, these research utilized a rodent mannequin of getting old mixed with acute intranasal administration of saline or OxA. Here, intranasal OxA will increase c-Fos expression in a number of telencephalic mind areas that mediate essential cognitive features, will increase prefrontal cortical acetylcholine efflux, and alters set-shifting-mediated attentional operate in rats.
Ultimately, these research present a framework for the potential mechanisms and therapeutic potential of intranasal OxA in treating age-related cognitive dysfunction.
The Neurochemistry of Autism.
Autism spectrum dysfunction (ASD) refers to advanced neurobehavioral and neurodevelopmental situations characterised by impaired social interplay and communication, restricted and repetitive patterns of conduct or pursuits, and altered sensory processing.
Environmental, immunological, genetic, and epigenetic elements are implicated in the pathophysiology of autism and provoke the incidence of neuroanatomical and neurochemical occasions comparatively early in the event of the central nervous system.
Many neurochemical pathways are concerned in figuring out ASD; nonetheless, how these advanced networks work together and trigger the onset of the core signs of autism stays unclear. Further research on neurochemical alterations in autism are essential to make clear the early neurodevelopmental variations behind the large heterogeneity of autism spectrum dysfunction, and due to this fact result in new approaches for the therapy and prevention of autism.
In this overview, we intention to delineate the state-of-the-art foremost analysis findings concerning the neurochemical alterations in autism etiology, and focuses on gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) and glutamate, serotonin, dopamine, N-acetyl aspartate, oxytocin and arginine-vasopressin, melatonin, vitamin D, orexin, endogenous opioids, and acetylcholine. We additionally intention to counsel a potential associated therapeutic strategy that would enhance the standard of ASD interventions.
Over 100 references have been collected by way of digital database looking out in Medline and EMBASE (Ovid), Scopus (Elsevier), ERIC (Proquest), PubMed, and the Web of Science (ISI).
