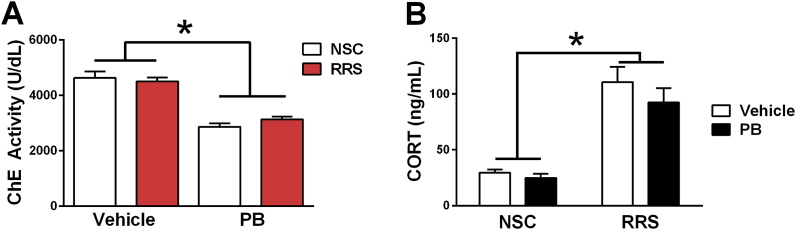
Pyridostigmine bromide (PB) was administered to troopers through the first Gulf War as a prophylactic therapy to guard towards toxicity within the occasion of publicity to nerve brokers. Although initially thought to pose minimal danger to troopers, epidemiological research have since correlated PB administration with the event of a selection of signs, together with cognitive dysfunction, termed Gulf War Illness (GWI).
We beforehand demonstrated in a rodent model of GWI that central cholinergic responses had been altered to numerous stimuli. In the present examine we used in vivo microdialysis to look at how combos of PB and repeated restraint stress (RRS) altered extracellular glutamate ranges in response to an innate immune problem (lipopolysaccharide; LPS) and an immobilization stress problem within the prefrontal cortex (PFC) and hippocampus.
There had been 4 teams on this examine: car non-stressed management (Veh-NSC), vehicle-stressed (Veh-RRS), PB-NSC, and PB-RRS.
While LPS decreased glutamate ranges in PB-treated rats relative to vehicle-treated rats within the PFC, PB and stress interacted to attenuate LPS-induced decreases in hippocampal glutamate ranges. Although immobilization stress elevated glutamate within the PFC, glutamate ranges in PB-NSC rats did not get well within the post-stress interval relative to vehicle-treated rats.
In the hippocampus, PB-stressed rats did not exhibit habituation of the glutamate response to immobilization stress relative to vehicle-stressed rats. Collectively, these outcomes point out that PB and stress interacted to provide brain-region particular results on glutamate neurochemistry, offering perception into the potential mechanisms underlying interactions between the immune system and persistent cognitive dysfunction in veterans with GWI.
Neurochemistry and subjunctivities of despair in Kerala, South India.
The narrative of despair as a neurochemical imbalance within the mind or, extra exactly, a deficiency of the neurotransmitters serotonin and norepinephrine – largely produced by business pursuits of the worldwide and nationwide pharmaceutical trade and unfold globally by worldwide diagnostic techniques – has discovered its approach into the workplaces of mainstream psychiatrists in Kerala. In the medical encounters, social, financial and existential struggling is thus remodeled into a medical situation, treatable with pharmacological means.
On the one hand, the setting of a psychiatric outpatient division largely shapes the best way depressive sufferers specific their subjectivities.
On the opposite hand, the analysis (and clarification) of despair as neurochemical imbalance and the prescription of medicine influences the best way sufferers expertise their struggling. Using two ethnographic examples, the intention of this paper is to investigate how subjectivities are construed and formed within the course of of negotiating despair in medical encounters in mainstream psychiatric establishments in Kerala and how a number of framings and ontologies of affliction are assembled in them.
Subjectivities of despair are, it will likely be argued, much less coherent than ambigious and fractured, unstable and fragile. They interact, intensify and generally merge completely different, usually contradictory discourses.
They ought to subsequently higher be known as ‘subjunctivities’. The idiom of despair usually turns into a rhetorical system to emphasise affiliation to a scientific medical discourse or citizenship and is usually a assertion to emphasise ‘scientific mood’ and modernity and to demarcate oneself from backwardness and superstition.
